3D Imaging Optical Filter
Friday, November29, 2024
3D Imaging Optical Filter
Ordinary cameras are 2D plane imaging, which loses the third dimension information in the physical world (geometric data such as size and distance). 3D imaging can identify the coordinate information of each point in space and realize various intelligent positioning.

There are three mainstream 3D imaging technologies:
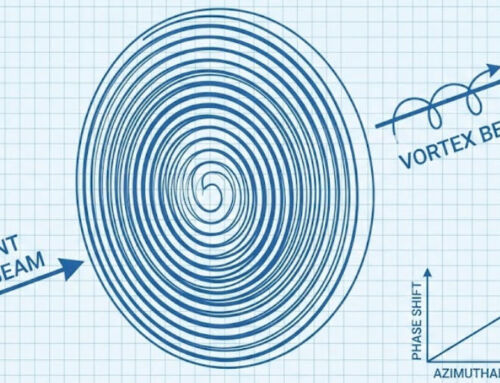
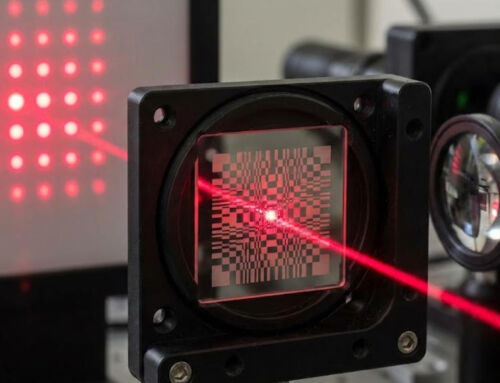
- Structured Light calculates the position and depth of the object according to the changes in the light signal caused by the object, and then restores the entire three-dimensional space.
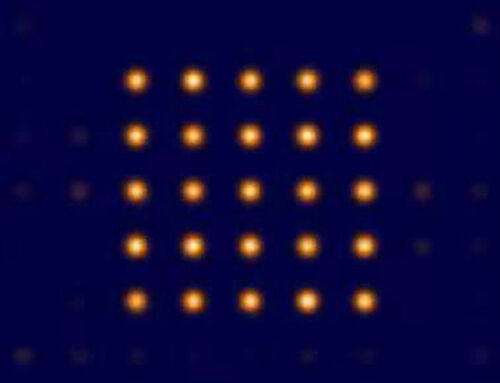
- TOF (Time Of Flight). Through a proprietary sensor, the flight time of near-infrared light from emission to reception is captured to determine the distance of the object.
- Stereo System. Use dual cameras to shoot objects, and then calculate the distance of the object through the triangle principle.
3D imaging technology depends on the 3D camera module. After the 3D camera module is disassembled, its main hardware includes: infrared light emitter (IR LED or VCSEL), infrared image sensor (IR CIS or other photodiodes) and visible light image sensor (Vis CIS), image processing chip, filter or lens.

The time-of-flight (ToF) solution for outdoor operation requires narrowband filters; the structured light solution requires an optical prism and a DOE grating at the transmitting end; the binocular stereo imaging solution uses two infrared cameras or two visible light cameras.

Narrowband filters play a key role in 3D imaging, helping to improve the clarity and accuracy of imaging. The band selection of 3D imaging narrowband filters (NBPF) is very wide and can be determined according to specific application requirements and technical specifications. Generally speaking, narrowband filters can achieve any wavelength within 350nm~2000nm.
Visible light band: such as 405nm, 450nm, 532nm, 635nm, etc. These bands are often used in 3D imaging systems based on visible light.
Near-infrared band: such as 850nm, 940nm, etc. These bands are widely used in 3D sensing and face recognition.
In addition, the main parameters of narrowband filters also include central wavelength, half-height width (bandwidth), peak transmittance, cut-off range and cut-off depth (OD value). The selection of these parameters will also affect the performance of the 3D imaging system. Therefore, when selecting narrowband filters, it is necessary to comprehensively consider these parameters and actual application requirements.
Coligh Optics has a large inventory of filters for sample prototype building and mass production. We are very experienced in the requirements of the camera industry for filters. If you are looking for filters for 3D cameras, please contact us
Product Categories
- Custom Optical Filter
- Custom Micro Optics
- Custom Infrared Optics